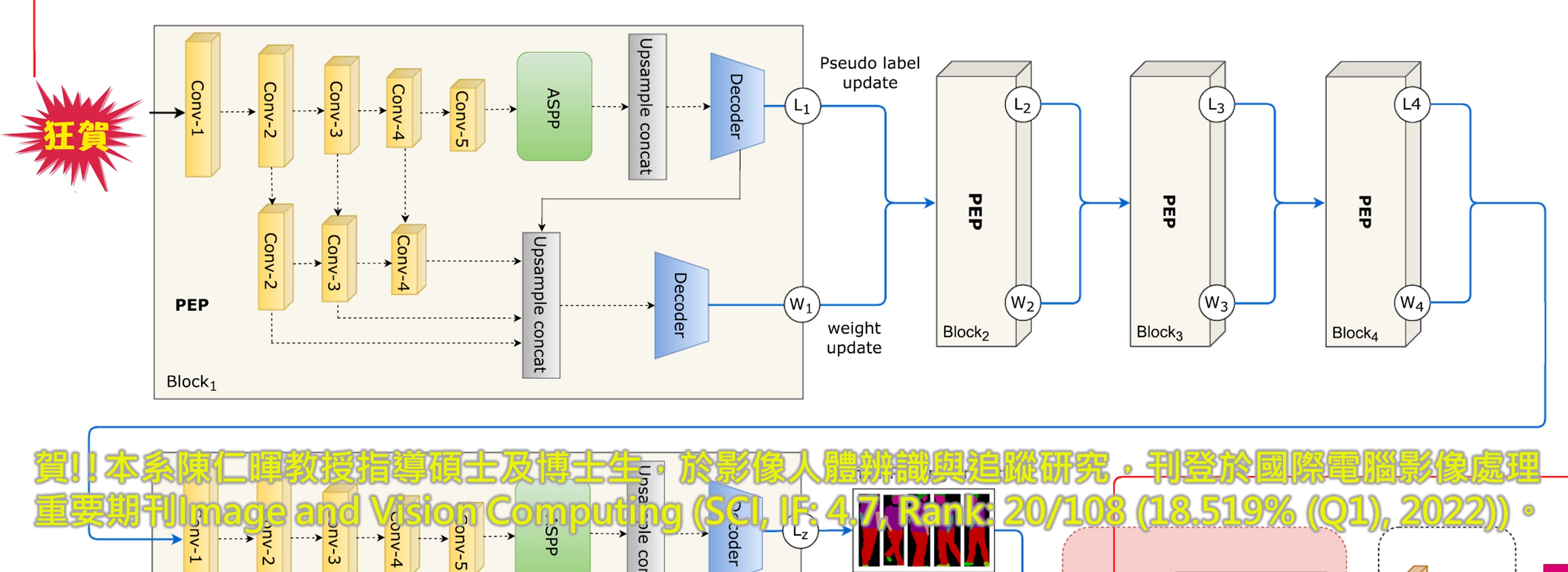
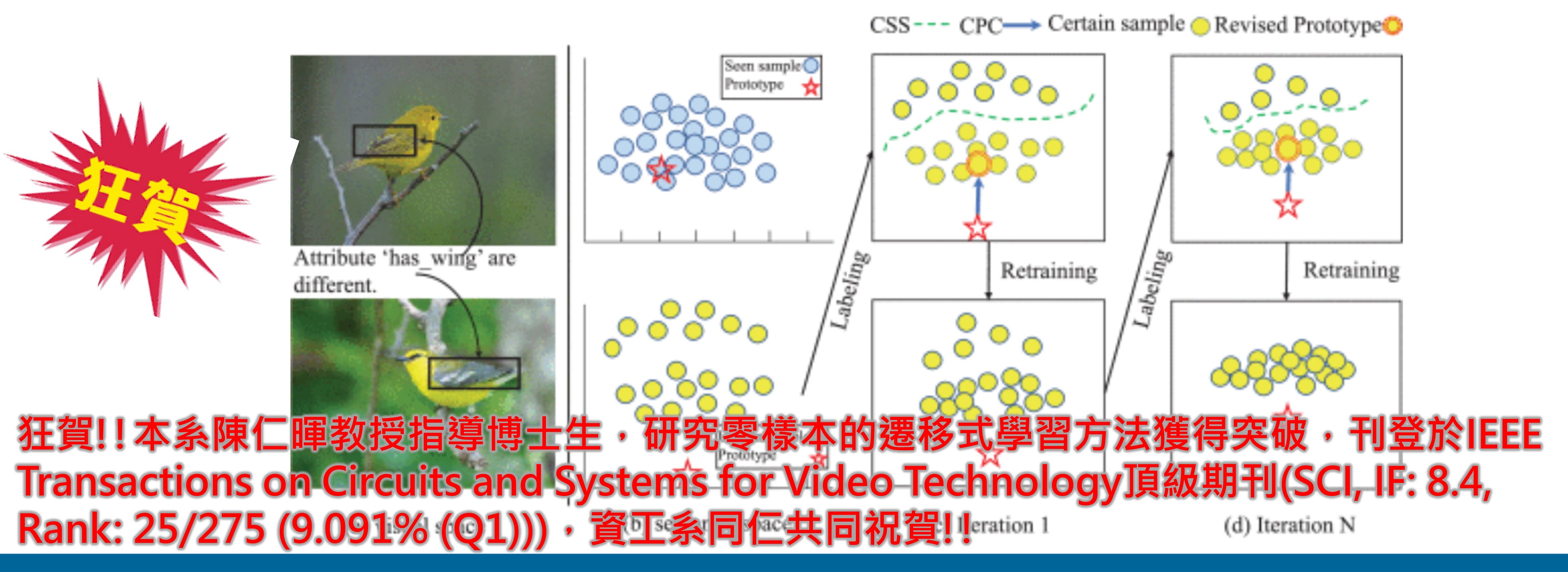
狂賀!!本系陳仁暉教授指導博士生,研究零樣本的遷移式學習方法獲得突破,刊登於IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology頂級期刊,資工系同仁共同祝賀!!
►狂賀!!本系陳仁暉教授指導博士生,研究零樣本的遷移式學習方法獲得突破,刊登於IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology頂級期刊(SCI, IF: 8.4, Rank: 25/275 (9.091% (Q1))),資工系同仁共同祝賀!!
Hairui Yang, Baoli Sun, Baopu Li, Caifei Yang, Zhihui Wang, Jenhui Chen, Lei Wang, and Haojie Li, "Iterative Class Prototype Calibration for Transductive Zero-shot Learning," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 1236-1246, March 2023. (SCI, IF: 8.4, Rank: 25/275 (9.091% (Q1), 2022) in Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3209209
Zero-shot learning (ZSL) typically suffers from the domain shift issue since the projected feature embedding of unseen samples mismatch with the corresponding class semantic prototypes, making it very challenging to fine-tune an optimal visual-semantic mapping for the unseen domain. Some existing transductive ZSL methods solve this problem by introducing unlabeled samples of the unseen domain, in which the projected features of unseen samples are still not discriminative and tend to be distributed around prototypes of seen classes. Therefore, how to effectively align the projection features of samples in unseen classes with corresponding predefined class prototypes is crucial for promoting the generalization of ZSL models. In this paper, we propose a novel Iterative Class Prototype Calibration (ICPC) framework for transductive ZSL which consists of a pseudo-labeling stage and a model retraining stage to address the above key issue. First, in the labeling stage, we devise a Class Prototype Calibration (CPC) module to calibrate the predefined class prototypes of the unseen domain by estimating the real center of projected feature distribution, which achieves better matching of sample points and class prototypes. Next, in the retraining stage, we devise a Certain Samples Screening (CSS) module to select relatively certain unseen samples with high confidence and align them with predefined class prototypes in the embedding space. A progressive training strategy is adopted to select more certain samples and update the proposed model with augmented training data. Extensive experiments on AwA2, CUB, and SUN datasets demonstrate that the proposed scheme achieves new state-of-the-art in the conventional setting under both standard split (SS) and proposed split (PS).
零樣本學習(ZSL)通常會遇到域轉移問題,因為未見樣本的投影特徵嵌入與相應的類語義原型不匹配,這使得針對未見域微調最佳視覺語義映射非常具有挑戰性。一些現有的轉導式 ZSL 方法透過引入未見域的未標記樣本來解決這個問題,其中未見樣本的投影特徵仍然不具有區分性,並且往往分佈在已見類的原型周圍。因此,如何有效地將未見類別中樣本的投影特徵與相應的預定義類別原型對齊對於促進ZSL模型的泛化至關重要。在本文中,我們提出了一種新穎的用於轉導式 ZSL 的迭代類原型校準(ICPC)框架,該框架由偽標記階段和模型再訓練階段組成,以解決上述關鍵問題。首先,在標記階段,我們設計了類原型校準(CPC)模組,透過估計投影特徵分佈的真實中心來校準未見域的預定義類原型,從而實現樣本點和類原型的更好匹配。接下來,在再訓練階段,我們設計了一個特定樣本篩選(CSS)模組,以高置信度選擇相對確定的未見過的樣本,並將它們與嵌入空間中預先定義的類別原型對齊。採用漸進式訓練策略來選擇更多確定的樣本,並以增強的訓練資料更新所提出的模型。對 AwA2、CUB 和 SUN 資料集的大量實驗表明,所提出的方案在標準分割(SS)和建議分割(PS)下的傳統設定中實現了新的最先進技術。